macrophage

What Drives Myeloid Cell Responses to Disease
The Scientist and Bio X Cell | Dec 17, 2024 | 4 min read
The TREM2 receptor may hold the keys to understanding how myeloid cells affect immune responses to neurological disorders and cancer.

Slow Bacterial Growth Enables Antibiotic Resistance
Niki Spahich, PhD | Aug 26, 2024 | 3 min read
In Salmonella, two seemingly similar antibiotic survival strategies result from very different molecular mechanisms.

Viral Research Gets Batty to Study Spillovers
Shelby Bradford, PhD | Aug 5, 2024 | 3 min read
Marburg virus enters humans from bats to cause viral hemorrhagic fever, but how it alters immune cells is unclear.

Aimless Monocytes Underlie a Rare Lung Disease
Niki Spahich, PhD | Apr 18, 2024 | 4 min read
Children with a multifaceted lung disorder share a receptor deficiency, which has implications for monocyte migration into the lungs.

Fish Oil in Diet Can Cause Hair Loss in Mice, Study Finds
Katherine Irving | Jan 19, 2023 | 3 min read
The oil’s omega-3 fatty acids accumulate in the mice’s skin, triggering an immune response that causes hair loss.

How Intracellular Bacteria Hijack Your Cells
Catherine Offord | Dec 1, 2022 | 10+ min read
Scientists studying pathogens such as Chlamydia, Legionella, and Listeria get a master class in how to control the internal workings of mammalian cells.

Infographic: Intracellular Bacteria’s Tricks for Host Manipulation
Catherine Offord | Dec 1, 2022 | 2 min read
Various microbes, including several human pathogens, hijack the cell’s skeleton, membranes, and protein-making machinery to make themselves at home.

Immune Cells Imitating Neurons Cause Pain in Mice with Tumors
Shafaq Zia | Oct 18, 2022 | 3 min read
Whether the finding of a novel mechanism for cancer-related pain can lead to better treatments for neuropathic pain in people remains to be seen.

Gonorrhea-Blocking Mutation Also Protects Against Alzheimer’s: Study
Holly Barker, PhD | Aug 5, 2022 | 4 min read
Research traces the evolution of a gene variant that reduces the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, finding that it originally evolved in response to infectious bacteria.

Cancer Cells Could Travel Through the Interstitium: Study
Marcus A. Banks | Apr 19, 2021 | 3 min read
The continuous network of fluid-filled compartments crosses organ barriers and might serve as a conduit for tumor cells to spread.

Microscopic Robots Deliver Drugs to the Brain
Asher Jones | Mar 30, 2021 | 5 min read
Researchers turned white blood cells called neutrophils into drug-smuggling “neutrobots,” which penetrated the blood-brain barrier to treat brain cancer in mice.

CAR Macrophages Tackle Challenges in Solid Cancer Treatment
Amanda Heidt | Mar 26, 2021 | 6 min read
Following on the success of CAR T cells used to treat cancers of the blood, researchers have launched a Phase 1 clinical trial of genetically modified macrophages to target solid tumors.

Understanding Transplant Rejection with Single-Cell Proteomics
The Scientist | Mar 9, 2021 | 1 min read
Researchers find key drivers of allograft rejection!

Infographic: Envisioning Macrophages
Ashley Yeager | Mar 1, 2021 | 1 min read
Researchers find different distributions of the immune cells in young, older, and diseased eyes.

Macrophages of the Human Eye Come into Focus
Ashley Yeager | Mar 1, 2021 | 3 min read
Imaged in real time in living people, immune cells at the surface of the retina could serve as biomarkers to detect retinal and possibly neurological diseases and track their progression.

A Tweak to Immune Cells Reverses Aging in Mice
Abby Olena, PhD | Jan 20, 2021 | 3 min read
Knocking out the receptor for a lipid that causes inflammation rejuvenates macrophage metabolism and restores cognitive function in an Alzheimer’s disease model.

Investigating the Immune Response Using Advanced Flow Cytometry
The Scientist | Oct 8, 2020 | 1 min read
Discover how researchers are using flow cytometry to delve into the inner workings of the immune life cycle!
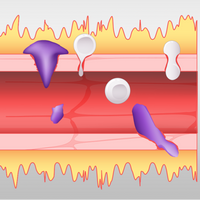
Is a Bradykinin Storm Brewing in COVID-19?
Alakananda Dasgupta | Aug 26, 2020 | 5 min read
Excess of the inflammatory molecule bradykinin may explain the fluid build-up in the lungs of patients with coronavirus infections. Clinical trials of inhibitors are putting this hypothesis to the test.
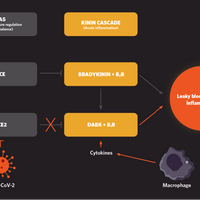
Infographic: SARS-CoV-2 Interferes with Bradykinin Regulation
Alakananda Dasgupta | Aug 26, 2020 | 1 min read
The leaky blood vessels and lung fluid build-up in some COVID-19 patients might be explained by the virus’s corruption of an inflammation safeguard.
