agriculture

Better Living Through Algae Biotechnology
Hannah Thomasy, PhD | Sep 13, 2024 | 10+ min read
Scientists explore how unicellular aquatic organisms could help humanity exist more sustainably.
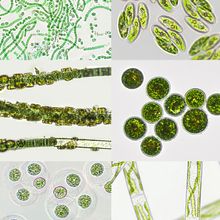
Algae: The Next Green Revolution
Hannah Thomasy, PhD | Sep 13, 2024 | 3 min read
Researchers explore algal biology for new strategies to help humans live more sustainably.

Low-Pass Whole Genome Sequencing: Revolutionizing Agriculture
The Scientist and MGI Tech | Sep 6, 2024 | 7 min read
By using low-pass whole genome sequencing, livestock breeders improve the accuracy, affordability, and speed of their breeding decisions.

As Carbon Dioxide Goes Up, Plants’ Nutrient Content Declines
Dan Robitzski | Nov 3, 2022 | 5 min read
Abundant environmental CO2 can increase plant biomass and photosynthesis, but it has downsides for agriculture and ecosystems, a growing body of research finds.

Pine Trees’ Fragrances Help Neighbors Battle Bark Beetles
Katherine Irving | Sep 30, 2022 | 5 min read
Polluted air impedes the trees’ ability to read one another’s signals, a study finds.

Genome Spotlight: Desert Locust (Schistocerca gregaria)
Christie Wilcox, PhD | Jul 21, 2022 | 4 min read
A chromosome-scale genome sequence for this infamous agricultural pest could help mitigate its plagues.

Climate Change and Agriculture Together Halve Insect Populations
Dan Robitzski | Apr 21, 2022 | 2 min read
Insect populations and species diversity are drastically reduced in areas affected by both climate change and agriculture-related habitat destruction, according to a new study.

Book Excerpt from Endangered Maize
Helen Anne Curry | Jan 17, 2022 | 4 min read
In Chapter 7, “Grow,” author Helen Anne Curry relays the story of Indigenous revolutionaries in Mexico who tapped into community-based methods to conserve traditional corn varieties.

Opinion: Going Beyond Seed Banks
Helen Anne Curry | Jan 17, 2022 | 5 min read
Rethinking why and how we conserve crop genetic diversity
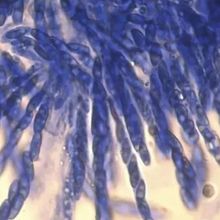
Researchers Resurrect Coffee-Destroying Fungus—to Study It
Chloe Tenn | Jan 4, 2022 | 4 min read
Comparing the genomes of modern pathogens with those of cryopreserved strains from several decades ago shed light on the evolution of coffee wilt disease outbreaks in Africa.

Contrary to Common Belief, Some Older Trees Make Fewer Seeds
Annie Melchor | Nov 1, 2021 | 2 min read
An analysis of more than half a million trees reveals that many species begin to taper off seed production once they hit a certain size.

Potty Party: Researchers Show Young Cows Can Be Toilet-Trained
Annie Melchor | Sep 14, 2021 | 6 min read
Ethologist Jan Langbein and his team trained the cattle as a way to keep solid and liquid cattle waste separate—with the goal of reducing ammonia emissions coming from livestock.

Genes Shared With Viruses Protect Caterpillars from Parasitic Wasps
Annie Melchor | Jul 30, 2021 | 4 min read
A newly identified gene family named “parasitoid killing factor” is found in both insect-infecting viruses and their hosts, although researchers can’t yet tell where they originated.

Hybrid Rice Developer Yuan Longping Dies at 90
Lisa Winter | May 26, 2021 | 2 min read
The high-yield variety of rice he produced in the 1970s prevented countless people from dying of starvation.

Stress-Response Compound Widespread in Animals Is Found in Plants
Shawna Williams | May 22, 2021 | 4 min read
TMAO appears to both stabilize other plant proteins and influence the expression of stress-response genes, researchers report.

Stamping Out Science, 1948
Catherine Offord | May 1, 2021 | 4 min read
Trofim Lysenko’s attacks on geneticists had long-term effects on Russian science and scientists, despite a lack of evidence to support his beliefs about biological inheritance.

Rediscovered Coffee Species Tastes Great, Tolerates Warmth: Study
Shawna Williams | Apr 20, 2021 | 2 min read
Cultivating stenophylla, untapped by the coffee industry for the last century, could help farmers cope with the effects of climate change, researchers suggest.

US Pesticide Use Is Down, but Damage to Pollinators Is Rising
Amanda Heidt | Apr 5, 2021 | 3 min read
The use of pesticides has decreased in the US by more than 40 percent since 1992, but the emergence of more-potent chemicals means that they are far more damaging to many species.

First Report of Horizontal Gene Transfer Between Plant and Animal
Emma Yasinski | Mar 25, 2021 | 3 min read
Whiteflies overcome a toxin in plants they eat through the use of the plant’s own genetic protection, likely ferried from plant to insect millions of years ago by a virus.
