blood clot

Hibernating Bears Provide Clue to Preventing Serious Clots in Humans
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Apr 13, 2023 | 3 min read
Low levels of the clotting factor HSP47 protect the sleeping giants from blood clots, and the same may be possible for humans and other mammals.

Multiple Possible Causes of Long COVID Come into Focus
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Sep 28, 2022 | 10+ min read
Recent studies have lent support for a variety of hypotheses explaining the debilitating symptoms affecting millions of people after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Genetic Variant Discovered in Amish Protects from Heart Disease
Abby Olena, PhD | Dec 2, 2021 | 3 min read
Researchers link a missense mutation in the B4GALT1 gene to lower levels of LDL cholesterol and the blood clotting factor fibrinogen.

Johnson & Johnson Vaccine Garners First Full Approval
Chloe Tenn | Nov 24, 2021 | 1 min read
Health Canada has given the single COVID-19 shot the official greenlight for use in people 18 and older.
Trapped Inflammatory Molecules Contribute to Long COVID
Roni Dengler, PhD | Nov 9, 2021 | 3 min read
Microclots in blood plasma may be behind Long COVID’s chronic symptoms.
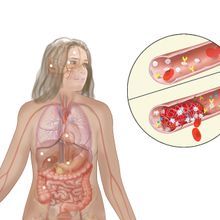
Infographic: The Havoc SARS-CoV-2 Wreaks on the Body
Diana Kwon | Sep 1, 2021 | 1 min read
COVID-19 affects far more than just the lungs. Researchers are actively documenting the damage the disease causes to the heart, brain, liver, and much more.
SARS-CoV-2’s Wide-Ranging Effects on the Body
Diana Kwon | Sep 1, 2021 | 8 min read
Researchers’ painstaking examinations have begun to reveal how the virus wreaks havoc in multiple organs and tissues.

Infographic: Pathways from Noise to Cardiovascular Damage
Thomas Münzel and Omar Hahad | Jun 1, 2021 | 2 min read
Research in mice and humans points to oxidative stress and inflammation as likely drivers of noise-induced health effects such as hypertension and heart disease.

How Environmental Noise Harms the Cardiovascular System
Thomas Münzel and Omar Hahad | Jun 1, 2021 | 10+ min read
Sound from cars, aircraft, trains, and other man-made machines is more than just annoying. It increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Blood Clot Risk from COVID-19 Higher than After Vaccines: Study
Shawna Williams | Apr 16, 2021 | 3 min read
The chance of developing cerebral venous sinus thrombosis was nearly 10 times higher in the two weeks following a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection than after receiving an mRNA vaccine, a data analysis finds.

US Health Authorities Ask for Pause in J&J COVID-19 Vaccination
Kerry Grens | Apr 13, 2021 | 2 min read
The FDA and CDC are investigating a handful of reports of blood clots that occurred several days after people received the one-and-done shot.

Blood Clots a Very Rare Side Effect of AstraZeneca Vaccine: EMA
Catherine Offord | Apr 8, 2021 | 2 min read
The European Medicines Agency emphasizes that the benefits of the jab in protecting against COVID-19 still far outweigh the risks.

The Brain on COVID-19
The Scientist | Dec 21, 2020 | 1 min read
Connecting the dots between COVID-19 and neurological disorders
Autopsies Indicate Blood Clots Are Lethal in COVID-19
Ashley Yeager | Jul 10, 2020 | 4 min read
A pathologist describes his observations from examining the bodies of those who succumbed to the coronavirus.

Could Statins Reduce the Severity of COVID-19?
Ashley Yeager | Jun 12, 2020 | 7 min read
The cholesterol-lowering drugs quell inflammation and reverse endothelial tissue damage, hints that they might curb the body’s excessive immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps May Augur Severe COVID-19
Alakananda Dasgupta | May 28, 2020 | 6 min read
These webs of chromatin and proteins, released by immune cells to control microbial infections, could serve as a therapeutic target in coronavirus infections.
Dog Study Revives Concerns About Virus Used for Gene Therapy
Jef Akst | Jan 6, 2020 | 2 min read
Canines treated with an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector showed evidence that the therapeutic DNA held within the virus can integrate into the host genome, risking the activation of oncogenes.

Image of the Day: Leprosy Lesion
The Scientist and The Scientist Staff | Mar 23, 2018 | 1 min read
Researchers identify two blood-clotting proteins that could be biomarkers for cardiovascular reactions in patients with leprosy.
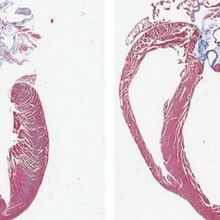
Image of the Day: Un-break My Heart
The Scientist | Aug 8, 2017 | 1 min read
A failing heart is easily distinguished from a healthy one by numerous tell-tale signs, including its slender, stretched-out walls, increased size, and pooled blood clots.
