blood
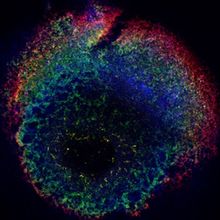
Scientists Get to the Heart of Blood Formation
Iris Kulbatski, PhD | Dec 11, 2024 | 4 min read
Researchers tweak heart-forming organoids to produce blood cells, in a process that mimics embryonic development.

Hibernating Bears Provide Clue to Preventing Serious Clots in Humans
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Apr 13, 2023 | 3 min read
Low levels of the clotting factor HSP47 protect the sleeping giants from blood clots, and the same may be possible for humans and other mammals.

Next-Level Neuroscience
The Scientist and MilliporeSigma | Sep 29, 2022 | 1 min read
Researchers use Single Molecule Counting (SMC®) technology to probe brain biomarkers.
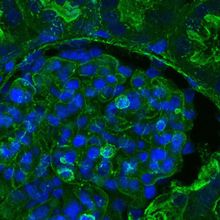
Artificial Blood Breathes New Life Into Dead Pigs’ Cells
Andy Carstens | Aug 3, 2022 | 2 min read
A study’s authors say their oxygenating cocktail may lead to technologies that preserve organs in deceased people for longer periods for transplantation.

Handmade Hemoglobin, 1912-2012
Dan Robitzski | Aug 1, 2022 | 3 min read
Makio Murayama, a Japanese-American biochemist who was turned away from the Manhattan Project due to his heritage, rose to prominence for his work uncovering the link between the structure of hemoglobin and the mechanisms of sickle cell disease.

Can Saliva Replace Blood for DNA Collection and Analysis?
DNA Genotek Inc. | Oct 27, 2021 | 1 min read
Saliva offers a less invasive and more cost-effective alternative for abundant high-quality DNA collection.
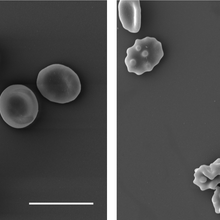
Red Blood Cells Activate Innate Immune System
Abby Olena, PhD | Oct 20, 2021 | 4 min read
Researchers link the ability of the cells to bind and present DNA from pathogens and cell death to anemia, which is common in COVID-19, and immune activation.

Low-Abundance Serum Proteins as Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Disease
SomaLogic | Jul 29, 2021 | 1 min read
Using deoxyoligonucleotides to bind proteins with high sensitivity and specificity

Technique Talk: Supporting Organoid Growth in 3D Cell Culture
The Scientist Creative Services Team in collaboration with Bio-Techne | Mar 8, 2021 | 1 min read
In this workshop, you will learn how to optimally culture organoids and support their growth after genetic manipulation.

Study Estimates 76 Percent of Brazilian City Exposed to SARS-CoV-2
Ignacio Amigo | Dec 14, 2020 | 6 min read
The number, extrapolated from antibodies present in blood donors in Manaus, should be treated with caution, experts warn.
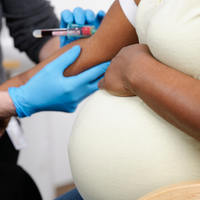
New RNA-Based Tool Could Assess Preeclampsia Risk
Amanda Heidt | Sep 1, 2020 | 2 min read
Transcripts circulating in the blood provide real-time information about maternal, fetal, and placental health.
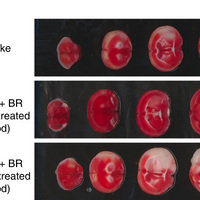
Blood Replacement Rescues Mice from Stroke Damage
Amanda Heidt | Aug 31, 2020 | 5 min read
When mice that had suffered a stroke were given blood from a healthy donor, they experienced less tissue and neurological damage.

FDA Gives Plasma Go-Ahead to Treat COVID-19, Experts Skeptical
Amanda Heidt | Aug 24, 2020 | 3 min read
White House officials hail convalescent plasma as a major breakthrough, but scientists say evidence supporting its effectiveness is still lacking.

The Father of Autoimmunity: A Profile of Noel Rose
Diana Kwon | Jun 1, 2020 | 9 min read
By revealing that animals could develop immune responses against their own tissues, the physician-scientist established an entirely new field of science.

Biogen Uses its Own Superspreader Event to Aid COVID-19 Research
Claire Jarvis | May 19, 2020 | 3 min read
A blood biobank allows scientists to study the immune responses to the coronavirus among infected Biogen employees and their contacts.
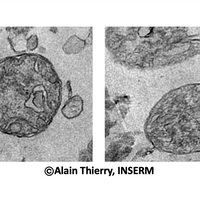
Researchers Find Cell-Free Mitochondria Floating in Human Blood
Katarina Zimmer | Feb 6, 2020 | 5 min read
The functional, respiring organelles appear to be present in the blood of healthy people, but their function is yet unclear.

Social Bonds Among Captive Vampire Bats Persist in the Wild
Emily Makowski | Nov 1, 2019 | 2 min read
Bats that share food with their hungry cage-mates stay close after being released.

Blood-Cleaning Machine Quickly Eliminates Carbon Monoxide in Rats
Ruth Williams | Oct 9, 2019 | 4 min read
A device that illuminates and oxygenates blood outside of the body before pumping it back in removes the gas by freeing hemoglobin from CO.

Cells’ Oxygen Sensing Discovery Earns Nobel Prize
Emily Makowski | Oct 7, 2019 | 2 min read
For the Physiology or Medicine award, Peter Ratcliffe, William Kaelin, and Gregg Semenza are credited with figuring out molecular and genetic responses to oxygen levels.
