hormones

Researchers Discover How Starfish Cut Ties with Their Limbs
Sneha Khedkar | Dec 4, 2024 | 4 min read
A neuropeptide helps starfish shed their arms to escape predators, providing clues about the mechanisms regulating self-amputation.

Bone-Building Hormone Identified in Lactating Mice
Claudia Lopez-Lloreda, PhD | Dec 3, 2024 | 4 min read
A brain-derived hormone that improves bone health could guide new treatments for age-related bone conditions.

The Importance of Water Purity when Studying Endocrine Disruptors
ELGA Veolia | Sep 19, 2024 | 1 min read
Detecting endocrine disrupting compounds for monitoring or characterization requires ultrapure water for consistent results.

Viral Immune Responses Suppress a Gestational Hormone
Shelby Bradford, PhD | Mar 25, 2024 | 4 min read
Influenza infection activates a pathway that leads to a detrimental drop in progesterone during pregnancy in mice.
The Brain's Barrier Controls Ant Behavior
Holly Barker, PhD | Nov 8, 2023 | 2 min read
Division of labor in ant colonies may depend on an enzyme trapped inside the blood-brain barrier.

Keeping Older Muscles Strong
Hannah Thomasy, PhD, Drug Discovery News | Sep 5, 2023 | 5 min read
From stem cell-recruiting gels to hormone cycle restoration, Tracy Criswell has big ideas about how to combat age-related decline in muscle regeneration.

Emergent Recombinant Proteins in Clinical Diagnostics
Scripps Laboratories | May 2, 2023 | 1 min read
A new era of reliable recombinant proteins makes it possible for researchers to replace tissue-derived biomarkers in a variety of diagnostic assays.
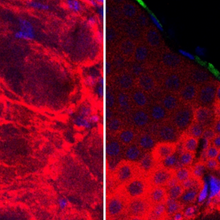
Gut Bacterium Linked to Depression in Premenopause
Alejandra Manjarrez, PhD | Mar 17, 2023 | 2 min read
The opportunistic pathogen Klebsiella aerogenes degrades estradiol and induces depressive-like behavior in mice, a study finds.
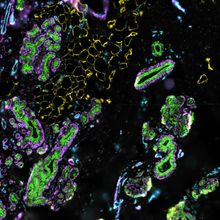
Hormone Therapy Triggers Male Gene Patterns in Transgender Men’s Cells
Holly Barker, PhD | Mar 15, 2023 | 3 min read
A study deepens the scientific understanding of how androgens influence breast tissue, which may offer clues to treating breast cancer.
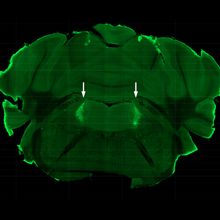
Hormone Sobers Up Drunken Mice: Study
Alejandra Manjarrez, PhD | Mar 8, 2023 | 3 min read
A hormone naturally induced by alcohol consumption accelerates the recovery of mice after binge drinking by activating neurons involved in arousal and alertness.

Monogamous Rodents Don’t Need “Love Molecule” To Pair Up
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Jan 27, 2023 | 4 min read
Prairie voles lacking functional receptors for oxytocin form normal social bonds, a finding that could explain the hormone’s clinical failures.

Scientists Use Centrifuge to Discover a Hormone
Katherine Irving | Jan 23, 2023 | 3 min read
A new method for isolating extracellular fluid aims to discover molecules with therapeutic potential that were previously obscured by highly abundant proteins.

The Scientist Speaks - What Comes Up Must Go Down: Maintaining Hormone Balance Through RNA Decay
The Scientist | Sep 22, 2022 | 1 min read
Neelanjan Mukherjee discusses how RNA decay is essential for regulating a blood pressure-controlling hormone.
Sex of Researcher Influences Ketamine’s Effects in Mice: Study
Shawna Williams | Sep 8, 2022 | 3 min read
The findings likely have implications for animal research far beyond the study of antidepressants.

Dogs Cry Tears of Joy: Study
Christie Wilcox, PhD | Aug 22, 2022 | 6 min read
Pet dogs produce a larger volume of tears when they are reunited with their owners than with acquaintances, possibly because of surging oxytocin levels—findings that could be the first evidence of emotional crying in nonhuman animals.

Steroids May Explain Octopuses’ Self-Starvation
Andy Carstens | May 16, 2022 | 2 min read
Two glands increase steroid production after female California two-spot octopuses mate, a study finds. Those hormones may be responsible for the animals’ self-destructive behavior.

Opinion: Can Science Capture Love?
Anna Machin | Mar 14, 2022 | 4 min read
Researchers who study the phenomenon in humans should incorporate subjective experiences into data on love.

Book Excerpt from Why We Love
Anna Machin | Mar 14, 2022 | 5 min read
In Chapter 1, “Survival,” author Anna Machin describes the health benefits of strong human bonds.

Measuring Hormones to Understand Metabolic Disorders
Bertin Instruments | Nov 8, 2021 | 1 min read
Researchers study obesity by assessing ghrelin levels in biological samples.
