cancer biology

2024 Top 10 Innovations
The Scientist Staff | Dec 13, 2024 | 10+ min read
The latest group of winning technologies has a little something for everyone—from scientists at the lab bench to those in the clinic and even the classroom.
One Protein to Rule Them All
Shelby Bradford, PhD | Feb 28, 2024 | 10+ min read
p53 is possibly the most important protein for maintaining cellular function. Losing it is synonymous with cancer.

Overcoming Genomic Analysis Challenges for Cancer Research
Oxford Nanopore Technologies | May 2, 2023 | 1 min read
Researchers advance the potential of precision medicine with cutting edge sequencing technology.
Bacterial Tractor Beams Bring Radiation to Tumors
Rachael Moeller Gorman | Apr 17, 2023 | 3 min read
Colonizing tumors with engineered bacteria may allow researchers to target sites currently inaccessible to radionuclide therapy.
Self-Charging Battery Battles Tumors in Mice
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Apr 4, 2023 | 3 min read
A battery that charges itself in salty fluids starves tumors of oxygen, helping improve some drugs treat cancer, a study finds.
Translation of “Jumping Genes” Creates Cancer Therapy Targets
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Mar 29, 2023 | 4 min read
Researchers find many tumor-specific antigens form when cancer genes and transposable elements link up.
Mutated Cohesin Throws DNA Splicing out of Whack, Resulting in Cancer
Shafaq Zia | Mar 3, 2023 | 2 min read
Cohesin mutations cause dysregulations in alternative splicing, contributing to tumor initiation and progression, a study finds.
Mutational Signature Indicates Risk of Kidney Cancer Recurrence
Holly Barker, PhD | Mar 1, 2023 | 2 min read
DNA sequencing can identify mutations that predict recurrence of renal cell carcinoma and may help low-risk patients avoid unnecessary treatment, a study finds.
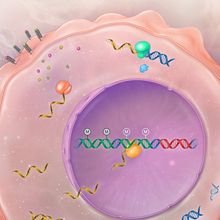
Infographic: Transposable elements in cancer
Diana Kwon | Mar 1, 2023 | 1 min read
Jumping genes are let loose in cancerous cells, with multiple effects on cell health.
Long noncoding RNAs and Microproteins Can Spark Cancer—or Sometimes Squelch It
Rachael Moeller Gorman | Mar 1, 2023 | 10+ min read
Noncoding RNAs and microproteins, once considered genomic noise, are turning out to be critical to the progression of some types of cancer.

Alex Muir Explores Cancer Cells’ Menu
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Mar 1, 2023 | 3 min read
The University of Chicago cell biologist is studying how the nutrients available to cancers influence their growth.
Jumping Genes’ Role in Cancer
Diana Kwon | Mar 1, 2023 | 8 min read
Transposons may be key players in how tumors develop and spread, but they also keep cancer at bay in some circumstances.
Jumping Genes Put a Target on Cancerous Cells
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Feb 14, 2023 | 4 min read
Two studies find that tumor-specific antigens are often peptides that result from a splicing event between exons and transposable elements.

Present Your Paper in The Scientist’s Journal Club
The Scientist Staff | Jan 9, 2023 | 1 min read
Apply today to share your cutting-edge research in The Scientist’s Journal Club.
Transfer RNAs Have a Surprising Role in Breast Cancer Growth
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Jan 5, 2023 | 4 min read
A particular leucine-ferrying tRNA is more abundant in cancerous cells than healthy ones, and lowering its levels inhibits cancer growth, a study finds.

Our Favorite Neuroscience Stories of 2022
Dan Robitzski | Dec 28, 2022 | 4 min read
This year, neuroscience researchers made important discoveries related to how neurodegeneration attacks the human brain, hooked cultured neurons up to machinery to teach them to play a video game, and more.
Our Favorite Cancer Stories of 2022
Dan Robitzski | Dec 27, 2022 | 4 min read
This year, cancer researchers uncovered a variety of ways that tumors can survive and spread, ranging from damaging their own DNA to exploiting the nearby microenvironment for nutrients.

Genome Spotlight: Fishing cat (Prionailurus viverrinus)
Christie Wilcox, PhD | Dec 22, 2022 | 5 min read
A high-quality reference genome for this vulnerable feline may help scientists understand why they’re so prone to transitional cell carcinoma in captivity.
Hypertranscription by Tumors Is Linked to Poorer Cancer Outcomes: Study
Sophie Fessl, PhD | Dec 13, 2022 | 3 min read
The extent to which transcription is higher in tumor cells than in surrounding nontumor cells is associated with bad prognoses in several cancer types.