imaging

2024 Top 10 Innovations
The Scientist Staff | Dec 13, 2024 | 10+ min read
The latest group of winning technologies has a little something for everyone—from scientists at the lab bench to those in the clinic and even the classroom.

Transforming 3D biology using AI: Tomocube’s HT-X1™ Plus accelerates cellular and organoids label-free analysis
Tomocube | Oct 31, 2024 | 2 min read
This new system raises the bar in high-resolution, high-throughput 3D imaging for cells and organoids, providing researchers with faster, more detailed, and more accurate insights into biological processes.

The Scientist’s Journal Club: Neuroscience and Cell Biology
The Scientist Staff | Mar 20, 2024 | 1 min read
Scientists discuss their latest findings on cell secretory states, synapse formation, and neurodegenerative disease.

Defining the Triple Negative Breast Cancer Morpholome
The Scientist Staff | Feb 21, 2024 | 1 min read
Learn how researchers take a phenotype-first approach to uncover hidden metastatic drivers at tissue and cellular levels.
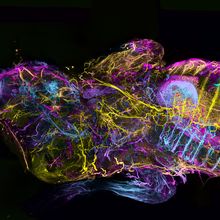
A Glowing Mouse Map
Mariella Bodemeier Loayza Careaga, PhD | Feb 1, 2024 | 2 min read
A whole-body immunostaining method allowed researchers to achieve cellular resolution at the whole-organism level.
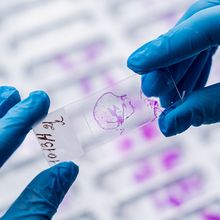
Advanced Spatial Tools Map Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niches
Niki Spahich, PhD | Jan 15, 2024 | 4 min read
New technologies and archival tissue biopsy samples enable exploration of changes in the bone marrow as people age.

Nobel Prize in Chemistry for Quantum Dots
Hannah Thomasy, PhD | Oct 4, 2023 | 3 min read
Moungi Bawendi, Louis Brus, and Alexei Ekimov were awarded the Nobel Prize for their work on quantum dots, which has applications in electronics and biomedicine.

Tackling the Challenges of Imaging-Based AI for Drug Development
Flywheel | Aug 31, 2023 | 1 min read
Scientists need streamlined data storage and sharing to automate drug discovery workflows.
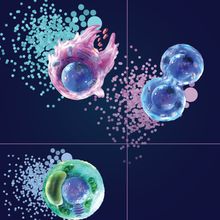
Sort What You See
BD Biosciences | Aug 29, 2023 | 1 min read
Camera-free imaging unlocks new cell sorting applications.

A Comprehensive Compilation of Western Blotting Best Practices
Cytiva | Aug 18, 2023 | 1 min read
Review tips to guide all stages of western blotting, from sample preparation to imaging and analysis.
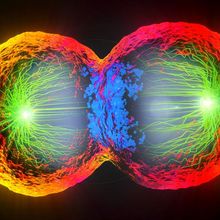
See Beyond the Scatter Plot with Imaging, Spectral Flow Cytometry
The Scientist and BD Biosciences | Aug 9, 2023 | 3 min read
A novel instrument combines fluorescence-activated cell sorting, imaging flow cytometry, and spectral flow cytometry to advance cell population examination.
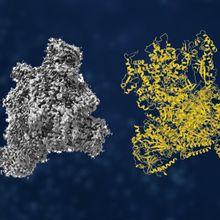
Cryo-EM: Building on a History of Invention and Innovation
Thermo Fisher Scientific | Aug 2, 2023 | 1 min read
From humble yet ingenious beginnings to Nobel recognition, cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) provides insights into scientific questions that other technologies are unable to answer.
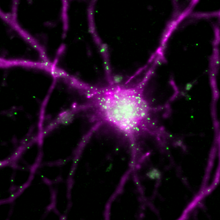
Short-lived Molecules Support Long-term Memory
Alejandra Manjarrez, PhD | Jun 6, 2023 | 3 min read
A gene essential for information storage in the brain engages an autoregulatory feedback loop to consolidate memory.

Data Management Tools for Greater Innovation and Discovery
Flywheel | Apr 4, 2023 | 1 min read
Discover the top five reasons researchers need modern medical imaging infrastructure.

2022 Top 10 Innovations
The Scientist | Dec 12, 2022 | 10+ min read
This year’s crop of winning products features many with a clinical focus and others that represent significant advances in sequencing, single-cell analysis, and more.

Obstetrics “Giant” Beryl Benacerraf Dies at 73
Katherine Irving | Oct 26, 2022 | 2 min read
Benacerraf pioneered the use of ultrasound to diagnose fetal syndromes.
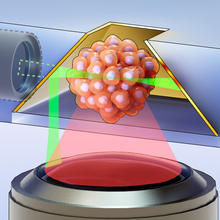
Infographic: Generating Hundreds of 3D Organoid Images per Hour
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Oct 17, 2022 | 1 min read
By modifying a technique used to image single cells, researchers have managed to generate a super-resolution 3D image of a complete organoid in just seven seconds.

Expert JeWell-ry Designers
Natalia Mesa, PhD | Oct 17, 2022 | 3 min read
Analyzing organoids has proven slow and cumbersome for scientists. But a new technique may speed things up, producing 3D images of hundreds of organoids per hour.

How To Select the Appropriate Biomolecular Imager
Cytiva | Sep 26, 2022 | 1 min read
Tips for matching the right imager to bioimaging workflows
